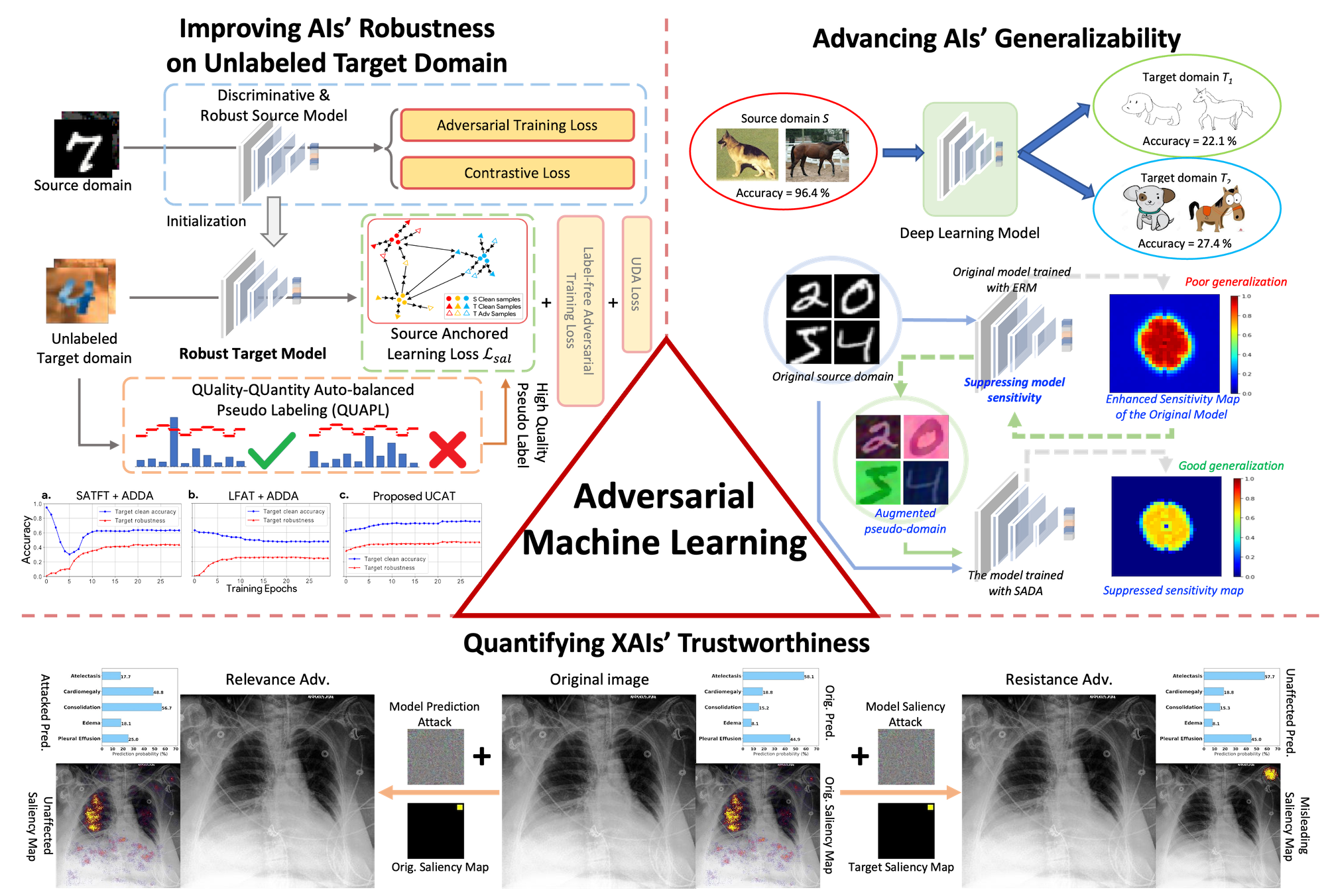
With the enormous amounts of data being acquired by large-scale healthcare systems, computational data analysis has become an essential component in healthcare applications to process and extract information. Deep learning, a sub-category of artificial intelligence (AI), has established itself as a paradigm-shifting technology for data analytics due to its powerful ability to extract high-level data representations. However, deep learning is known to be vulnerable to adversaries, which cause algorithms to yield dramatically different results by making very small alterations to input data samples. Adversaries are particularly hazardous in medical imaging applications where an altered image may lead an AI algorithm to cause medical errors. Thus, there is an urgent need to innovate and build robust healthcare cyberinfrastructure to guard against deep learning adversaries. This project develops novel AI techniques to tackle the unprecedented challenges of adversaries in medical imaging applications from a systematic standpoint. It brings awareness to potential issues when implementing AI in healthcare and develops new tools to mitigate these issues. This research will bolster confidence in adopting AI to improve healthcare efficiency and will also attract and train the next generation of AI researchers and engineers.
This project aims to develop innovative AI techniques to systematically mitigate deep learning adversaries in medical imaging applications. This project is timely as deep learning is already widely used in image reconstruction, quality enhancement, computer-aided diagnosis, and image-guided intervention and surgery. Several challenges, including detection and rectification of adversaries as well as robust algorithm training across data domains, must be resolved before achieving robust medical imaging applications. Existing methods are concerned with only the deep learning algorithms themselves and try to build universal blind robustness against arbitrary adversaries, which overlooks upstream data characteristics and downstream task specifics. This research adopts a holistic approach and is organized around a series of integrated subtopics, including detecting individual adversarial images, differentiating adversarial images from different sources, rectifying adversarial images, determining the transferability of robustness across data domains, and quantifying output uncertainties. The research will provide new insights, accurate yet robust AI techniques, and novel strategies to improve the robustness of medical imaging applications.