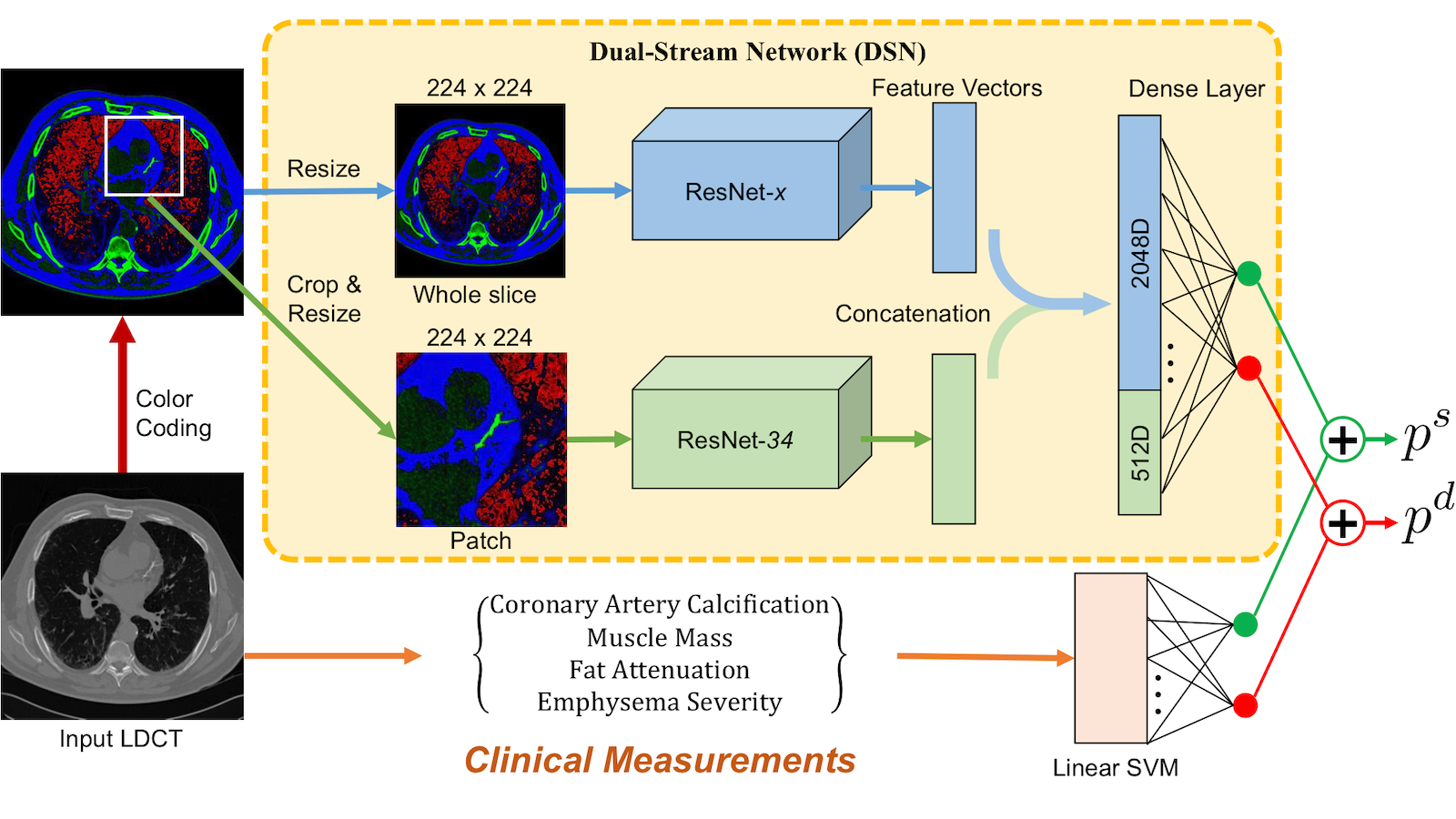
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) caused 17.7 million deaths in 2015, accounting for one third of all deaths globally. Amongst 8.8 million cancer-deaths in 2015, lung cancer contributed to 1.69 million deaths worldwide. In the United States, lung cancer will claim 154,050 lives in 2018, representing a quarter of all cancer deaths. Both CVDs and lung cancer share several risk factors, including unhealthy dietary patterns, obesity, and tobacco use. The goal of the project is to develop an automated workflow of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risk (CARMOR) evaluation with lung cancer screening LDCT data to provide high-risk subjects a “radiation-free” CVD screening without cost or time constraints. Our central hypothesis is that deep radiomics from LDCT follow-up scans and across different reconstructions can effectively improve the performance of CARMOR estimation.
This work is supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award R56HL145172.